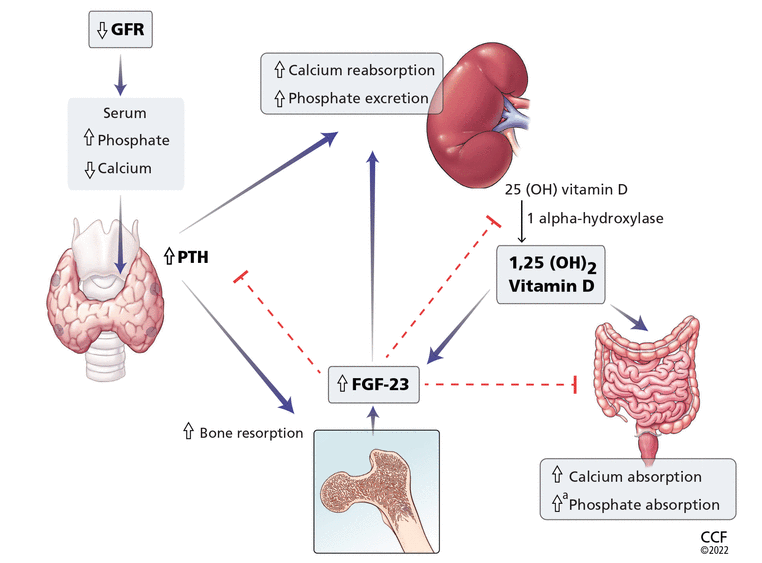
In the February 2022 issue, in Bartolomeo K, Tan XY, Fatica R. Extraosseous calcification in kidney disease. Cleve Clin J Med 2022; 89(2):81–90. doi:10.3949/ccjm.89a.21073, an error appeared in Figure 1 on page 83, relative to phosphate excretion and phosphate absorption. The correct figure appears below:
Calcium and phosphate metabolism in chronic kidney disease. Decreased glomerular filtration rate (GFR) leads to changes in serum calcium and phosphate, triggering release of parathyroid hormone (PTH) from the parathyroid glands and fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF-23) from osteoblasts and osteocytes. These hormones have complex downstream effects on the kidney, gut, and bone, both from direct effects on the tissue and from indirect effects through modulation of enzyme activity in vitamin D conversion.
aMinimally increased.
25(OH) vitamin D = 25-hydroxycholecalciferol; 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D = 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
This is now correct on ccjm.org.
- Copyright © 2022 The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. All Rights Reserved.