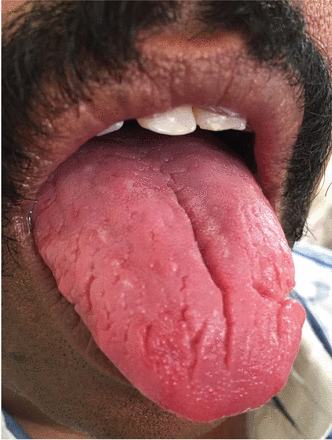
A 43-year-old man presented with a 3-week history of halitosis. He was also concerned about the irregular appearance of his tongue, which he had noticed over the past 3 years. He had no history of wearing dentures or of any skin disorder.
On examination, he had poor oral hygiene and deep fissures on his tongue (Figure 1). A diagnosis of fissured tongue was made, and the patient was prescribed oral chlorhexidine gargles 3 times a day for 1 week. He was reassured of the benign nature of the condition and was educated about the need for good oral hygiene.
The fissures, present for the past 3 years, were asymptomatic.
A BROAD DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Fissured tongue (scrotal tongue, plicated tongue, lingua plicata) is a common normal variant of the tongue surface with a male preponderance and a reported prevalence of 10% to 20% in the general population, and the incidence increases strikingly with age.1
The cause is not known, but familial clustering is seen, and a polygenic or autosomal dominant hereditary component is presumed.1
The condition may be associated with removable dentures, geographic tongue, pernicious anemia, Sjögren syndrome, psoriasis, acromegaly, macroglossia, oral-facial-digital syndrome type I, Pierre Robin syndrome, Down syndrome, and Melkersson Rosenthal syndrome.2 It is usually asymptomatic, but if the fissures are deep, food may become lodged in them, resulting in tongue inflammation, burning sensation, and halitosis.1
Typically, fissures of varying depth extending to the margin are apparent on the dorsal surface of the tongue. The condition is confined to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, which is of ectodermal origin. Histologically, the epithelium, lamina propria, and musculature are all involved in the formation of the fissures.3 The deeper fissures may lack filliform papillae due to bacterial inflammation.3 The diagnosis is clinical, and treatment includes reassurance, advice on good oral hygiene, and tongue cleansing.1
- © 2019 The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. All Rights Reserved.