A 22-year old man with no cardiac history presented to our emergency department after 5 days of dyspnea, cough, vomiting, and sharp intermittent epigastric pain. He used marijuana chronically and had inhaled it in unusually high amounts for several days before the onset of his symptoms.
The physical examination was unremarkable. Diagnostic tests including a complete blood cell count, complete metabolic panel, lipase level, urinalysis, and chest radiography showed no notable abnormalities. A urine drug screen revealed marijuana use.
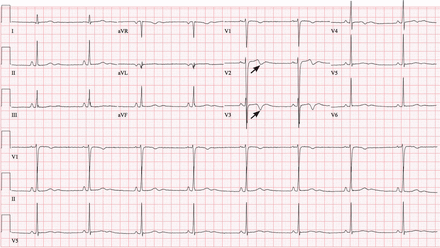
Electrocardiography (Figure 1) showed a heart rate of 49 beats per minute, new bi-phasic T-wave inversions in leads V2 and V3, normal precordial R-wave progression, and absent Q waves. His troponin T level was less than 0.01 ng/mL (reference range 0.0–0.29). Echocardiography showed a normal ejection fraction and no wall-motion abnormalities.
The patient’s electrocardiogram showed new biphasic T-wave inversions in leads V2 and V3 (arrows), normal precordial R-wave progression, and absent Q waves.
Given this clinical picture, the question was whether cardiac catheterization was needed. Our young, previously healthy patient lacked risk factors for coronary artery disease and did not present with chest pain. Though dyspnea and epigastric pain are angina equivalents, he did not have the profile of patients commonly presenting with angina. Further, acute marijuana intoxication has been reported to be associated with reversible changes affecting the P and T waves and ST segments.1,2 The likelihood of critical occlusion of the left anterior descending artery in this patient was deemed low.
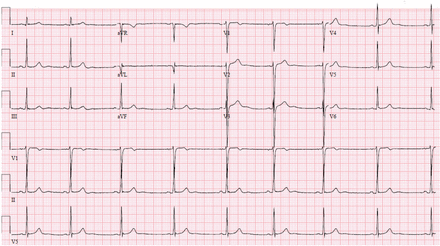
He was diagnosed with acute marijuana intoxication and discharged after 1 day of improvement. He never returned for follow-up, but a follow-up phone call 1 week later confirmed that the symptoms had resolved. Electrocardiography 7 months later during another visit to the emergency department for epigastric pain showed resolution of the T-wave changes (Figure 2).
Electrocardiography 7 months later showed resolution of T-wave inversions.
PSEUDO-WELLENS SYNDROME
Wellens syndrome is characterized by biphasic or deeply inverted T waves in leads V2 and V3, normal precordial R-wave progression, and the absence of pathologic Q waves, in addition to a history of angina and minimal or no elevation of cardiac enzymes in a patient with or without ongoing chest pain.3,4 This ominous syndrome is associated with critical occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending artery whose natural history is anterior myocardial infarction in the next few days. Stress testing is contraindicated, and urgent catheterization is warranted to prevent progression to myocardial infarction, even in patients without known heart disease or multiple cardiac risk factors.5
This case shows that acute marijuana intoxication may present with symptoms typical of Wellens syndrome. Because Wellens syndrome is considered highly specific for impending anterior myocardial infarction, urgent cardiac catheterization typically would be recommended. In this age of increasing use and legalization of marijuana, knowledge of the electrocardiographic findings associated with heavy marijuana use may prevent unnecessary cardiac catheterization procedures, especially in patients at low risk.
- Copyright © 2017 The Cleveland Clinic Foundation. All Rights Reserved.